
Introduction
Code on Github: Elasticsearch and Beats
We will setup Heartbeat with Elasticsearch and Kibana. If you do not have Elasticsearch and Kibana set up yet, then follow these instructions.
This video assumes you are using Publicly Signed Certificates. If you are using Self Signed Certificates, go here TBD.
Requirements
A running instance of Elasticsearch and Kibana.
An instance of another Ubuntu 20.04 server running any kind of service.
Steps
Step 1 - Download Heartbeat [01:12]
On the Ubuntu machine that will run packetbeat, run these commands to download dependencies:
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg;
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https;
echo 'deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/8.x/apt stable main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-8.x.list;
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y heartbeat-elastic;
Step 2 - Configure Heartbeat [02:21]
Edit these fields for the /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml.
heartbeat.monitors:
- type: http
# ID used to uniquely identify this monitor in elasticsearch even if the config changes
id: apache-website
# Human readable display name for this service in Uptime UI and elsewhere
name: Apache Website
# List or urls to query
urls: ["<url>"] #["http://192.168.0.60"]
# Configure task schedule
schedule: '@every 5s'
# Total test connection and data exchange timeout
#timeout: 16s
# Name of corresponding APM service, if Elastic APM is in use for the monitored service.
#service.name: my-apm-service-name
- type: http
# ID used to uniquely identify this monitor in elasticsearch even if the config changes
id: elastic-rest
# Human readable display name for this service in Uptime UI and elsewhere
name: Elastic Rest
# List or urls to query
urls: ["<elasticsearch-domain>:<elasticsearch-port>"]
username: 'elastic'
password: "<your elastic password>"
# Configure task schedule
schedule: '@every 5s'
setup.kibana:
host: "https://<kibana-domain>:<kibana-port>"
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["<elasticsearch-domain>:<elasticsearch-port>"]
protocol: "https"
username: "elastic"
password: "<your elastic password>"
Completed heartbeat.yml can be found here
IMPORTANT - we are using the elastic super user for the initial set up and configuration. We will downgrade the privileges later.
Then test your configuration with these commands:
/usr/share/heartbeat/bin/heartbeat test config -c /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml --path.data /var/lib/heartbeat --path.home /usr/share/heartbeat
/usr/share/heartbeat/bin/heartbeat test output -c /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml --path.data /var/lib/heartbeat --path.home /usr/share/heartbeat
You should see something like this:
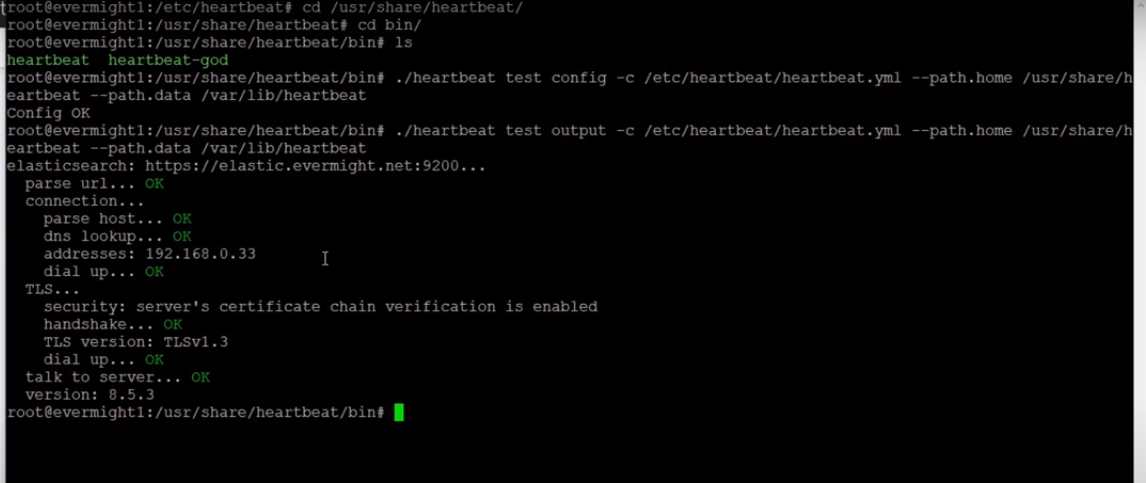 Verify heartbeat configuration
Verify heartbeat configuration
Step 3 - Setup Heartbeat [12:48]
Now run this command to set up heartbeat datastreams and views in Elasticsearch and Kibana:
/usr/share/heartbeat/bin/heartbeat setup -c /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml --path.data /var/lib/heartbeat --path.home /usr/share/heartbeat
Once the command finishes, go to Kibana Menu and visit Observability > Overview to see a Monitor section.
Step 4 - Create a Publishing User [14:53]
Create Heartbeat Data View [16:18]
In Kibana, go to Stack Management > Data Views. Click on create data views and fill in following fields:
name: heartbeat-*
index: heartbeat-*
Timestamp field: @timestamp
and then click on save data view to kibana
Create Role
In Kibana, go to Stack Management > Roles > Create role. Then fill out these fields:
Role name: heartbeat-publisher
Cluster privileges: monitor, read_ilm
Indices: heartbeat-*
Privileges: create_doc
Create User
In Kibana, go to Stack Management > Users > Create user. Then fill out these fields:
Username: heartbeat-publisher
Full name: heartbeat-publisher
Email address: anything@anything.com
Password: anything
Roles: heartbeat-publisher, editor
Create API Key for User
In Kibana, go to Dev Tools > Console. Then run this command:
POST /_security/api_key/grant
{
"grant_type": "password",
"username": "heartbeat-publisher",
"password": "anything",
"api_key": {
"name": "heartbeat-publisher"
}
}
This should produce a result like:
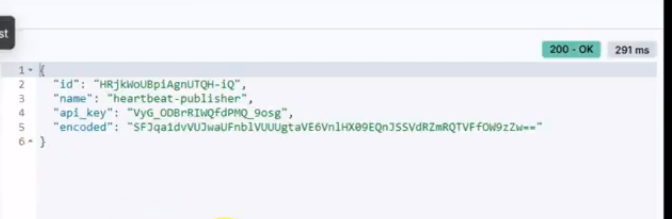 Heartbeat user token
Heartbeat user token
Edit the /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml by commenting out the elastic username and password and enabling the api_key like so:
output.elasticsearch:
...etc...
api_key: "${ES_API_KEY}"
#username: "elastic"
#password: ""
...etc...
We will be using the heartbeat keystore to load secrets for run time. Now run this command to set the ES_API_KEY keystore variable:
/usr/share/heartbeat/bin/heartbeat keystore add ES_API_KEY -c /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml --path.data /var/lib/heartbeat --path.home /usr/share/heartbeat
Press enter and when prompted, paste in <id>:<api_key> where the <id> and the <api_key> are the values from the user token response you got previously.
Step 5 - Run Heartbeat [17:37]
systemctl enable heartbeat-elastic;
systemctl start heartbeat-elastic;
In a moment, you should start seeing results in Kibana in either Discover, Observability, Stack Management > Observability > Monitors.
Step 6 - Setup another monitor without having to reload Heartbeat [26:15]
On the terminal, go to
cd /etc/heartbeat/monitors.d
then copy one of the disabled template
cp sample.html.yml.disabled html.yml.disabled
Open up the file
vi html.yml.disabled
It should look like this:
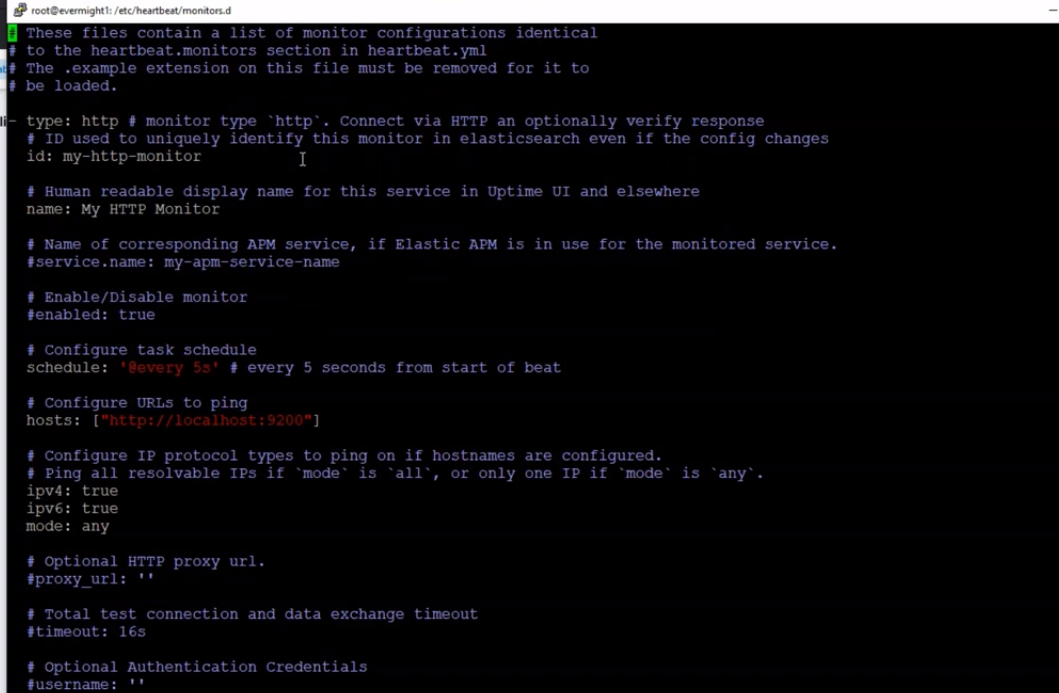 Heartbeat new http monitor
Heartbeat new http monitor
And then make corresponding changes
id: Any id
name: Any name
schedule: Any type of schdule, though i will use cron as an example
hosts: ["<the monitor url>]
The image below shows an example:
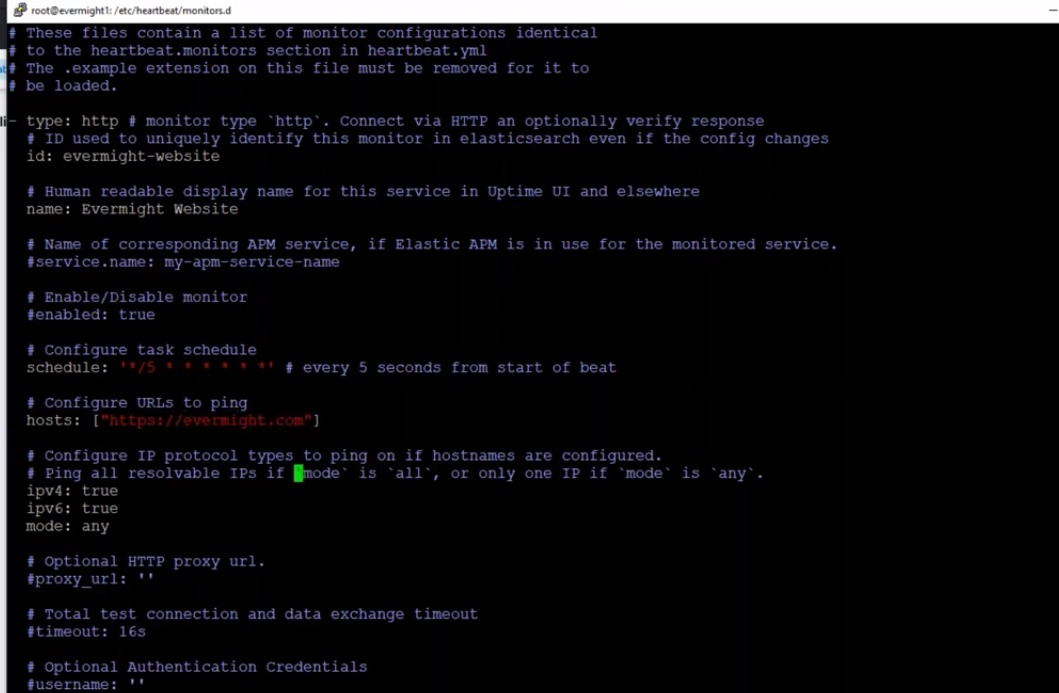 Heartbeat new http monitor example
Heartbeat new http monitor example
Now to enable it, we can use the below command
cp html.yml.disabled html.yml
Step 7 - Setup a second observer [28:24]
On another server/machine follow step 1, and then continue with the commands to copy the files from the first server to this new/current server as shown in the below image:
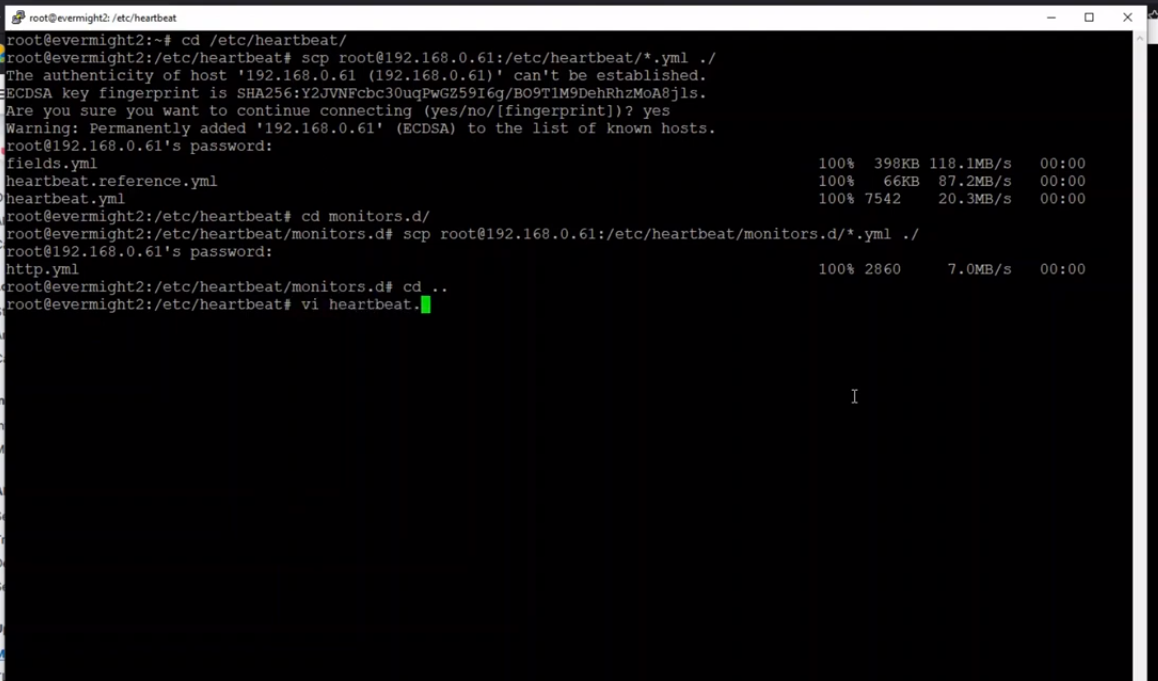 Heartbeat Second Observer to copy files from original server to current one
Heartbeat Second Observer to copy files from original server to current one
and then edit these fields for the /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml
Below is an example image:
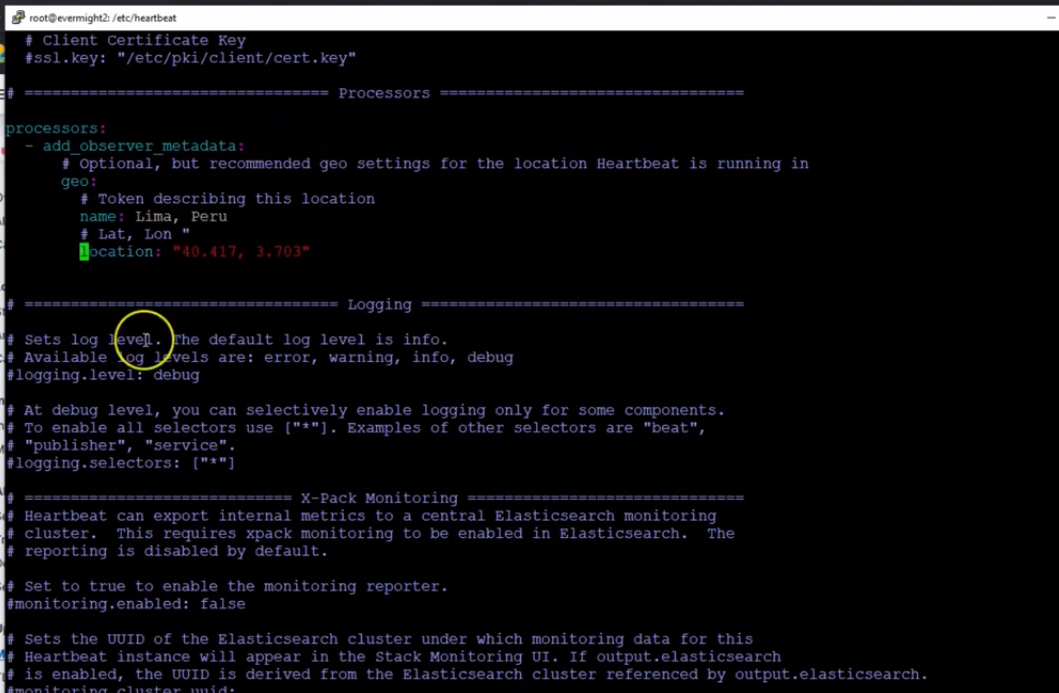 Heartbeat Second Observer heartbeat.yml file edits
Heartbeat Second Observer heartbeat.yml file edits
We will be using the heartbeat keystore to load secrets for run time. Now run this command to set the ES_API_KEY keystore variable:
/usr/share/heartbeat/bin/heartbeat keystore add ES_API_KEY -c /etc/heartbeat/heartbeat.yml --path.data /var/lib/heartbeat --path.home /usr/share/heartbeat
Press enter and when prompted, paste in <id>:<api_key> where the <id> and the <api_key> are the values from the user token response you got previously.
Now run Heartbeat
systemctl enable heartbeat-elastic.service;
systemctl start heartbeat-elastic.service;
